To put it in the most elementary terms, the accounting equation is the guiding principle of every financial transaction. It is, as we all know, also the very foundation and the most fundamental thought-theory behind the double-entry bookkeeping system, in order to help maintain whatever true and fair view of the company’s accounts appears to lie in the equation.
Whether one is an owner, a student, or an aspiring accountant, the understanding of an accounting equation is essential for the understanding of financial statements, with particular reference to their construction and interpretation.
What Is the Accounting Equation?
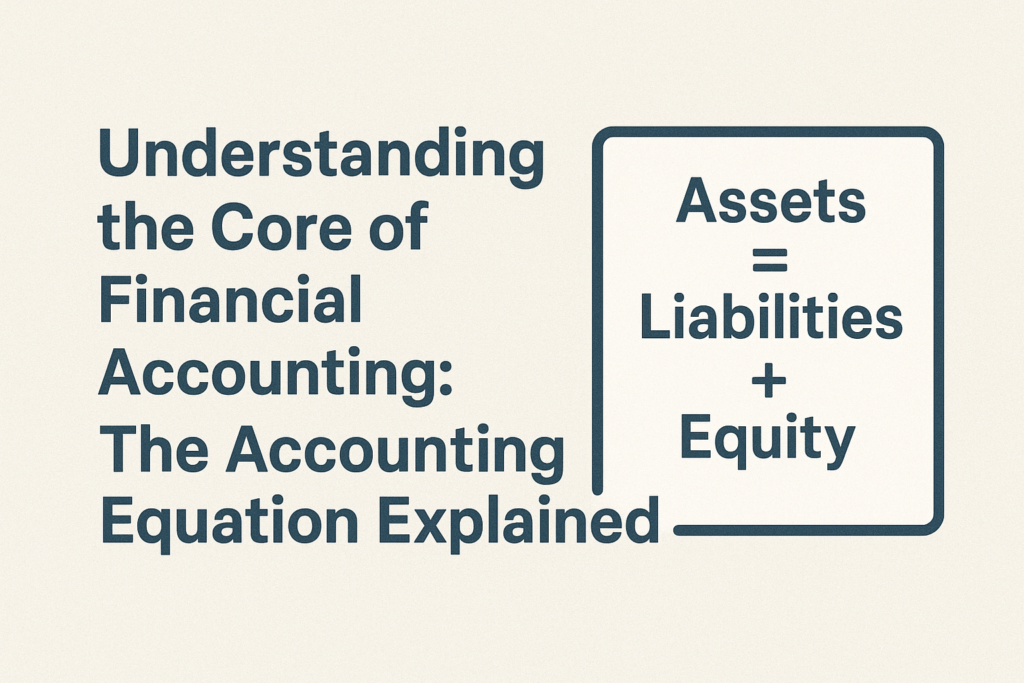
The accounting equation is:
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity
Here, the accounting equation expresses the relation between the business assets (what it owns), liabilities (what it owes), and the owner’s equity (the owner’s interest in the business). The perspective of each part will be taken, and the operation of the accounting equation will be discussed, along with practical examples:
Key Components of the Accounting Equation
- Assets – Assets refer to the resources that are owned by businesses and have economic value. Cash, inventory, and machinery to accounts receivable are calculated as assets. Assets represent the total value of all the items that a company controls and uses to generate revenue.
- Liabilities – On the other hand, liabilities are the debts and obligations that a business has to pay to an outside party. Liabilities are used to show the claims of creditors on the assets of businesses. Loans, accounts payable and mortgages are included in this section.
- Owner’s Equity – The last part of an accounting equation is owner’s equity, which is also known as the shareholders’ equity. It is the interest left with the owner after all the liabilities are paid. It includes invested capital and retained earnings (profits reinvested in the business).
Calculated as: Owner’s Equity = Assets – Liabilities
How Does an Accounting Equation Work?
Along with knowing what is the accounting equation, you should also know how the equation works.
- Maintains Balance
- Since every transaction affects at least two different accounts, it upholds the integrity of the equation.
- For example, purchasing equipment with cash reduces the amount of cash one has; however, it increases assets in the form of equipment.
- Double-Entry System
- The accounting equation forms the main structure of double-entry bookkeeping.
- Every transaction affects two different accounts: debit and credit, to ensure accuracy and balance.
- Guides Financial Reporting
- The balance sheet is the main financial statement of any organisation, and this is made using the accounting equation.
- It provides a picture of the financial position of the company at a specific date.
- Helps Identify Errors
- If the equation does not balance, there is an error involved in the transactions recorded.
- In this way, it provides an excellent form of internal control and accuracy for the financial statements.
Conclusion
Accounting equation means more than just a formula- it is the very foundation upon which the whole financial accounting architecture stands. The accounting equation is used to highlight the relationship between the assets, liabilities and the equity of the owner. This ensures that every transaction is balanced and duly recorded. The accounting equation assets liabilities is an equation which represents the assumption of success of any organisation.
Visit us: accountinglads.com