Topical Anesthetics are essential medications used to numb the skin and reduce pain during various medical and cosmetic procedures. From tattoo sessions and waxing to minor surgical treatments, Topical Anesthetics offer quick, non-invasive pain relief that helps patients stay comfortable without the need for injections. These creams, gels, and sprays temporarily block nerve signals in the skin, making them a reliable choice for anyone seeking safe and effective pain management solutions.
What Are Topical Anesthetics?
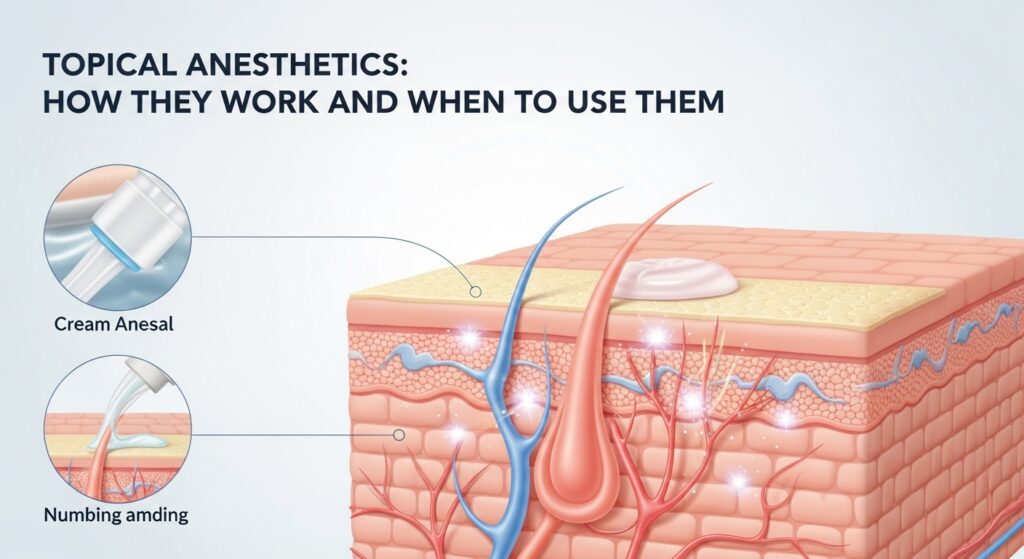
Topical anesthetics are medications applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb a specific area and prevent pain. They work by blocking the nerve signals that transmit pain sensations to the brain. Unlike injectable local anesthetics, topical versions are non-invasive and ideal for minor procedures or short-term relief.
These medications are available in several forms, including creams, gels, sprays, and patches, and are often used in dermatology, dentistry, and cosmetic treatments. Common active ingredients include lidocaine, benzocaine, prilocaine, and tetracaine, each offering different strengths and durations of action.
For example:
- Lidocaine is one of the most widely used ingredients in topical anesthesia for its fast-acting properties and safety profile.
- Benzocaine is popular for treating minor skin irritations and oral discomfort.
- Prilocaine and tetracaine are often used in combination for medical or aesthetic procedures requiring deeper numbing.
How Do Topical Anesthetics Work?
Topical anesthetics work by temporarily blocking sodium channels in the skin’s nerve endings. This prevents the nerves from sending pain signals to the brain, resulting in a localized numbing effect.
When applied, the anesthetic penetrates the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) and acts on the underlying nerve endings. The effect usually begins within 15 to 30 minutes of application, depending on the product and concentration, and can last anywhere from 30 minutes to two hours.
Key factors that influence effectiveness include:
- The concentration of the active ingredient (e.g., 2% vs. 5% lidocaine)
- The skin’s thickness and sensitivity
- The duration of application before the procedure
- Whether the area is covered with an occlusive dressing to enhance absorption
Common Uses of Topical Anesthetics
Topical anesthetics are used in a wide range of settings from medical clinics to spas and even at home.
Medical Uses
In clinical environments, topical anesthetics help minimize pain during:
- Blood draws, vaccinations, or IV insertions
- Minor surgical or dermatological procedures
- Cleaning and dressing minor wounds or burns
Cosmetic and Aesthetic Uses
They’re also frequently used in beauty treatments to make procedures more comfortable:
- Tattooing and micropigmentation
- Laser hair removal and waxing
- Micro-needling and chemical peels
In all these applications, numbing creams like lidocaine-based topical anesthetics ensure patients experience minimal discomfort, improving the overall experience.
Types of Topical Anesthetics
Topical anesthetics come in several formulations, each suited for different needs:
- Creams and Ointments – Ideal for larger skin areas; commonly used before tattoos, waxing, or dermatological treatments.
- Gels – Used for both skin and mucous membranes (e.g., in dentistry or minor oral irritations).
- Sprays – Provide quick, convenient numbing for small or sensitive areas.
- Patches – Deliver steady pain relief over a controlled time period for minor injuries or localized pain.
You can find both over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription-strength topical anesthetics. OTC products typically contain 2-4% lidocaine and are suitable for general use. Prescription creams, such as EMLA (lidocaine + prilocaine), are stronger and intended for medical or professional procedures.
How to Apply Topical Anesthetics Safely
Proper application is essential for both safety and effectiveness. Follow these steps for best results:
- Clean the area – Wash and dry the skin to remove oils or debris.
- Apply a thin, even layer – Use the recommended amount as stated on the product label.
- Cover if necessary – For deeper numbing, cover the area with plastic wrap (occlusive dressing) as directed.
- Wait the recommended time – Usually 15-45 minutes before the procedure.
- Remove residue – Wipe off any excess cream before starting the treatment.
Avoid applying topical anesthetics on broken skin, open wounds, or near the eyes unless the product is specifically designed for those areas.
Safety Tips and Possible Side Effects
While topical anesthetics are generally safe when used correctly, misuse or overapplication can cause side effects such as:
- Skin redness or irritation
- Swelling or itching
- Allergic reactions
- In rare cases, toxicity from excessive absorption (especially with high-concentration lidocaine products)
People with certain medical conditions such as heart disease, liver problems, or skin sensitivity should consult a healthcare provider before using these products.
Topical Anesthetics vs. Local Anesthetics
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, topical and local anesthetics differ in application and effect:
- Topical anesthetics are applied on the surface and work by numbing only the outer skin layers.
- Local anesthetics, like lidocaine injections, are administered under the skin to numb deeper tissues for surgical or dental procedures.
Topical anesthetics are ideal for minor pain relief, while local anesthetics are used for more invasive procedures.
FAQs About Topical Anesthetics
Q1: How long before a procedure should I apply topical anesthetic?
Apply it 20-45 minutes before the procedure, depending on the product’s strength and instructions.
Q2: Are topical anesthetics safe for sensitive skin?
Yes, most are safe if used correctly. However, always test a small patch first to check for reactions.
Q3: Can I use topical anesthetics for tattoos and waxing?
Absolutely. Lidocaine-based creams are commonly used for both tattoos and waxing to reduce discomfort.
Q4: What is the strongest over-the-counter topical anesthetic available in Canada?
Most OTC products contain up to 5% lidocaine, which is the maximum allowed without a prescription.
Q5: How often can I apply topical anesthetic?
Use only as directed typically no more than three to four times daily, and never on large areas for extended periods.
Conclusion
Topical anesthetics are an invaluable part of modern pain management, offering fast, safe, and effective relief for a variety of skin-related procedures. By understanding how they work, their proper use, and their limitations, you can confidently manage discomfort during both medical and cosmetic treatments.
For those seeking compounded topical anesthetics tailored to individual needs such as specific lidocaine concentrations or custom formulations Aurora Compounding Pharmacy provides high-quality, personalized solutions designed with safety, precision, and comfort in mind.
Whether you’re a healthcare provider or someone preparing for a cosmetic procedure, choosing the right topical anesthetic from a trusted compounding pharmacy ensures optimal results and peace of mind.